Why “Chanakya”?
Arya Chanakya: Perhaps the pioneering prime bureaucrat- scholar. The thinker who realized the dangers of foreign invasion. Chanakya Mandal Pariwar has tried to awaken a corrupt exploitative, anti-people and inefficient regime. When the power-drunk corrupt regime refused to wake up, he sacrificed his career, went into wilderness organized and inspired the young generation from the commonest of the common strata of society.
He affected the political revolution which unified India and repulsed the foreign invasion. Having achieved all this he renounced all positions of power and wrote the eternal treatise ‘Artha Shastra’.
Qualifying Papers On Indian Languages And English
Note 1:
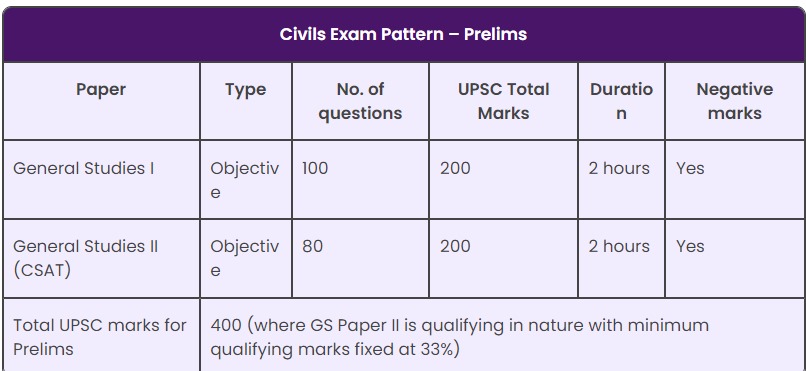
Paper-II of the Civil Services (Preliminary) Examination
will be a qualifying paper with minimum qualifying
marks fixed at 33%.
Note 2:
The questions will be of multiple choice, objective type.
Note 3:
It is mandatory for the candidate to appear in both the
Papers of Civil Services (Prelim) Examination for the
purpose of evaluation. Therefore a candidate will be
disqualified in case he/she does not appear in both the
papers of Civil Services (Prelim) Examination.
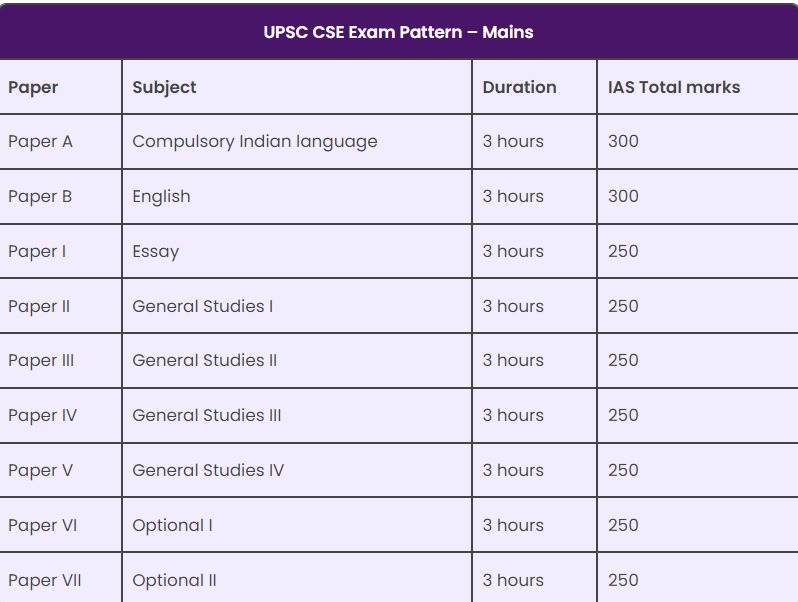
PAPER-IV
General Studies-III: Technology, Economic Development, Bio diversity, Environment, Security and Disaster Management
1. Indian Economy and issues relating to planning, mobilization, of resources, growth, development and employment.
2. Inclusive growth and issues arising from it.
3. Government Budgeting.
4. Major crops-cropping patterns in various parts of the
country, – different types of irrigation and irrigation systems storage, transport and marketing of agricultural
produce and issues and related constraints; e-technology in the aid of farmers.
5. Issues related to direct and indirect farm subsidies and
minimum support prices; Public Distribution Systemobjectives, functioning, limitations, revamping; issues
of buffer stocks and food security; Technology missions; economics of animal-rearing.
6. Food processing and related industries in India- scope’
and significance, location, upstream and downstream
requirements, supply chain management.
7. Land reforms in India.
8. Effects of liberalization on the economy, changes in industrial policy and their effects on industrial growth.
9. Infrastructure: Energy, Ports, Roads, Airports, Railways
etc.
10. Investment models.
11. Science and Technology- developments and their applications and effects in everyday life.
12. Achievements of Indians in science & technology; indigenization of technology and developing new technology.
13. Awareness in the fields of IT, Space, Computers, robotics, nano-technology, bio-technology and issues relating to intellectual property rights.
14. Conservation, environmental pollution and degradation, environmental impact assessment.
15. Disaster and disaster management
16. Linkages between development and spread of extremism.
17. Role of external state and non-state actors in creating
challenges to internal security.
18. Challenges to internal security through communication
networks, role of media and social networking sites in
internal security challenges, basics of cyber security;
money-laundering and its prevention.
19. Security challenges and their management in border
areas – linkages of organized crime with terrorism.
20. Various Security forces and agencies and their mandate.
PAPER-V
General Studies- IV: Ethics, Integrity and Aptitude
1. This paper will include questions to test the candidates’
attitude and approach to issues relating to integrity,
probity in public life and his problem solving approach
to various issues and conflicts faced by him in dealing with society. Questions may utilise the case study
approach to determine these aspects. The following
broad areas will be covered :
2. Ethics and Human Interface: Essence, determinants and
consequences of Ethics in-human actions; dimensions
of ethics; ethics – in private and public relationships.
Human Values – lessons from the lives and teachings
of great leaders, reformers and administrators; role of
family society and educational institutions in inculcating values.
3. Attitude: content, structure, function; its influence and
relation with thought and behaviour; moral and political attitudes; social influence and persuasion.
4. Aptitude and foundational values for Civil Service, integrity, impartiality and non-partisanship, objectivity,
dedication to public service, empathy, tolerance and
compassion towards the weaker-sections.
5. Emotional intelligence-concepts, and their utilities and
application in administration and governance.
6. Contributions of moral thinkers and philosophers from
India and world.
7. Public/Civil service values and Ethics in Public administration: Status and problems; ethical concerns and
dilemmas in government and private institutions; laws,
rules, regulations and conscience as sources of ethical guidance; accountability and ethical governance;
strengthening of ethical and moral values in governance; ethical issues in international relations and
funding; corporate governance.
8. Probity in Governance: Concept of public service; Philosophical basis of governance and probity; Information
sharing and transparency in government, Right to Information, Codes of Ethics, Codes of Conduct, Citizen’s
Charters, Work culture, Quality of service delivery, Utilization of public funds, challenges of corruption.
9. Case Studies on above issues.
PAPER-V
General Studies- IV: Ethics, Integrity and Aptitude
1. This paper will include questions to test the candidates’
attitude and approach to issues relating to integrity,
probity in public life and his problem solving approach
to various issues and conflicts faced by him in dealing with society. Questions may utilise the case study
approach to determine these aspects. The following
broad areas will be covered :
2. Ethics and Human Interface: Essence, determinants and
consequences of Ethics in-human actions; dimensions
of ethics; ethics – in private and public relationships.
Human Values – lessons from the lives and teachings
of great leaders, reformers and administrators; role of
family society and educational institutions in inculcating values.
3. Attitude: content, structure, function; its influence and
relation with thought and behaviour; moral and political attitudes; social influence and persuasion.
4. Aptitude and foundational values for Civil Service, integrity, impartiality and non-partisanship, objectivity,
dedication to public service, empathy, tolerance and
compassion towards the weaker-sections.
5. Emotional intelligence-concepts, and their utilities and
application in administration and governance.
6. Contributions of moral thinkers and philosophers from
India and world.
7. Public/Civil service values and Ethics in Public administration: Status and problems; ethical concerns and
dilemmas in government and private institutions; laws,
rules, regulations and conscience as sources of ethical guidance; accountability and ethical governance;
strengthening of ethical and moral values in governance; ethical issues in international relations and
funding; corporate governance.
8. Probity in Governance: Concept of public service; Philosophical basis of governance and probity; Information
sharing and transparency in government, Right to Information, Codes of Ethics, Codes of Conduct, Citizen’s
Charters, Work culture, Quality of service delivery, Utilization of public funds, challenges of corruption.
9. Case Studies on above issues.
PAPER-VI & PAPER VII
Optional Subject Papers I & II
Candidate may choose any optional subject from amongst the List of Optional Subjects given
UPSC-PAPER-1: Essay
 CTS
CTS  Donate
Donate 


